Online Ads
/
Taze Creative
A banner ad is a type of online advertisement that appears as a graphic display on websites, aimed at attracting the attention of visitors and encouraging them to click through to the advertiser's website or landing page.
Banner ads come in a variety of sizes and formats, ranging from static images to animated graphics. Vertical banner ads are typically referred to as "skyscrapers," while horizontal ones are called "leaderboards."
These ads are often used to promote products, services, events, or to increase brand awareness. The effectiveness of a banner ad depends on factors such as its design, placement, and relevance to the target audience.
Like other forms of advertising, banner ads use visual elements to capture the attention of online users and motivate them to take a specific action. Here’s how they operate:
Ad Creation The process begins with designing visually engaging banner ads, which typically combine images, text, and sometimes interactive features. The design's goal is to grab attention and deliver a clear message about the product or service being promoted.
Ad Placement Advertisers then select specific websites or platforms that are popular among their target audience. These ads are placed in high-visibility spots like above the main content, in sidebars, or between paragraphs. When users visit these websites, the ads are dynamically fetched from an ad server and displayed in real time.
User Interaction Banner ads usually contain a clickable element, often a call to action or the entire ad itself. When users click on the ad, they are directed to the advertiser's website or a specific landing page. Website owners hosting the ads are compensated in one of three ways:
Cost per click (CPC): Payment for each click on the ad.
Cost per impression (CPM): Payment per thousand views of the ad.
Cost per action (CPA): Payment for specific user actions, like purchases or form submissions.
Analytics Advertisers track performance through metrics such as click-through rates (CTR), impressions, and conversions. These insights help evaluate the success of the campaign.
Targeting Advertisers can target their audience based on factors like demographics, interests, or browsing history. This ensures the ads are shown to users who are most likely to engage with the product or service. Retargeting is also used, where users who interacted with the ad but didn’t complete a desired action (such as a purchase) are shown similar ads as they navigate other websites.
In summary, the effectiveness of banner ads depends on a mix of eye-catching design, strategic ad placement, and precise targeting to achieve the advertiser’s goals.
Here are the most common types of banner ads:
1. Static banner ads
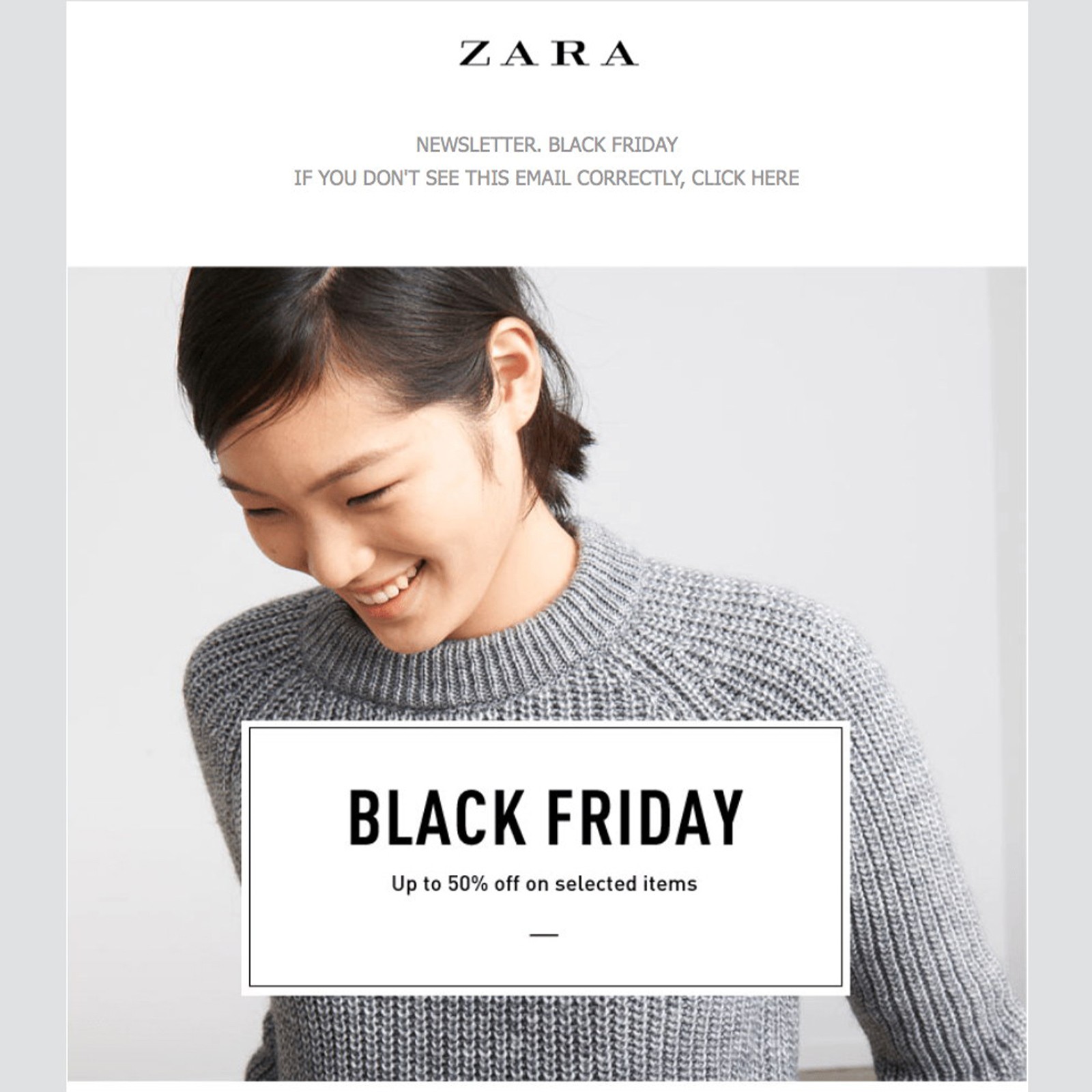
As the name suggests, static banner ads feature non-moving images that convey a straightforward message. They're perfect for building brand awareness, showcasing products, or delivering a simple call to action. Their minimalist design allows the message to be absorbed instantly without the distraction of animation. Example: Clorox’s banner ad highlights product images and a clear value proposition for its cleaning products.
2. Animated banner ads image

Animated banner ads include movements like fading, sliding, or rotating elements to create a more engaging experience. These ads can tell a brief story or highlight multiple messages in a single ad space. The animations often help emphasize key features, promotions, or create a sense of urgency.
Example: Design Studio’s animated banners feature various jackets at discounted prices, using movement to grab attention.
3. Video banner ads
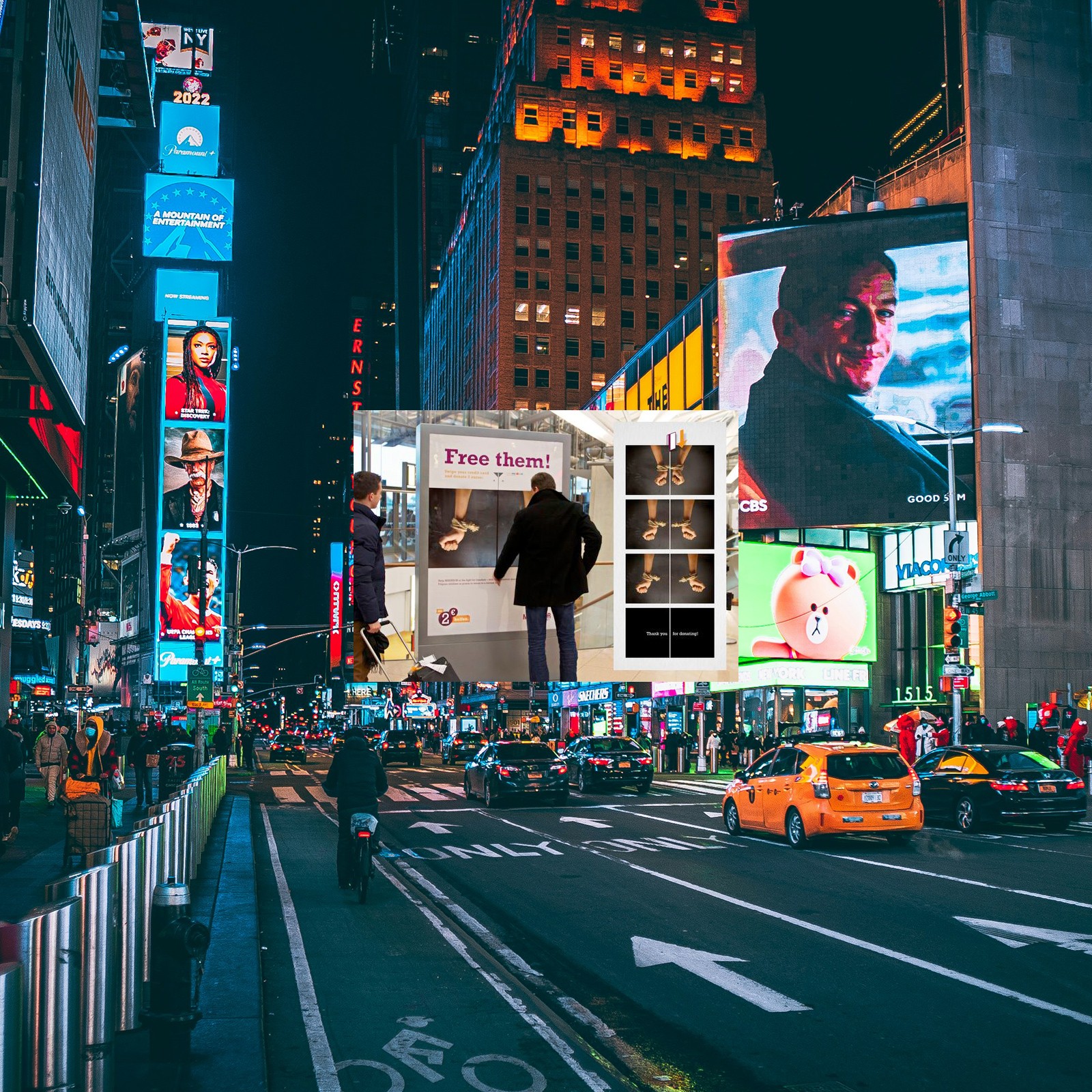

Video banner ads contain short video clips that automatically play when the webpage loads or when the user interacts with them. These ads combine moving images and sound to create impactful audiovisual storytelling, making them ideal for product demonstrations or brand narratives.
Example: A video banner ad showcasing interior design services uses video to convey a more immersive message.
4. Interactive banner ads
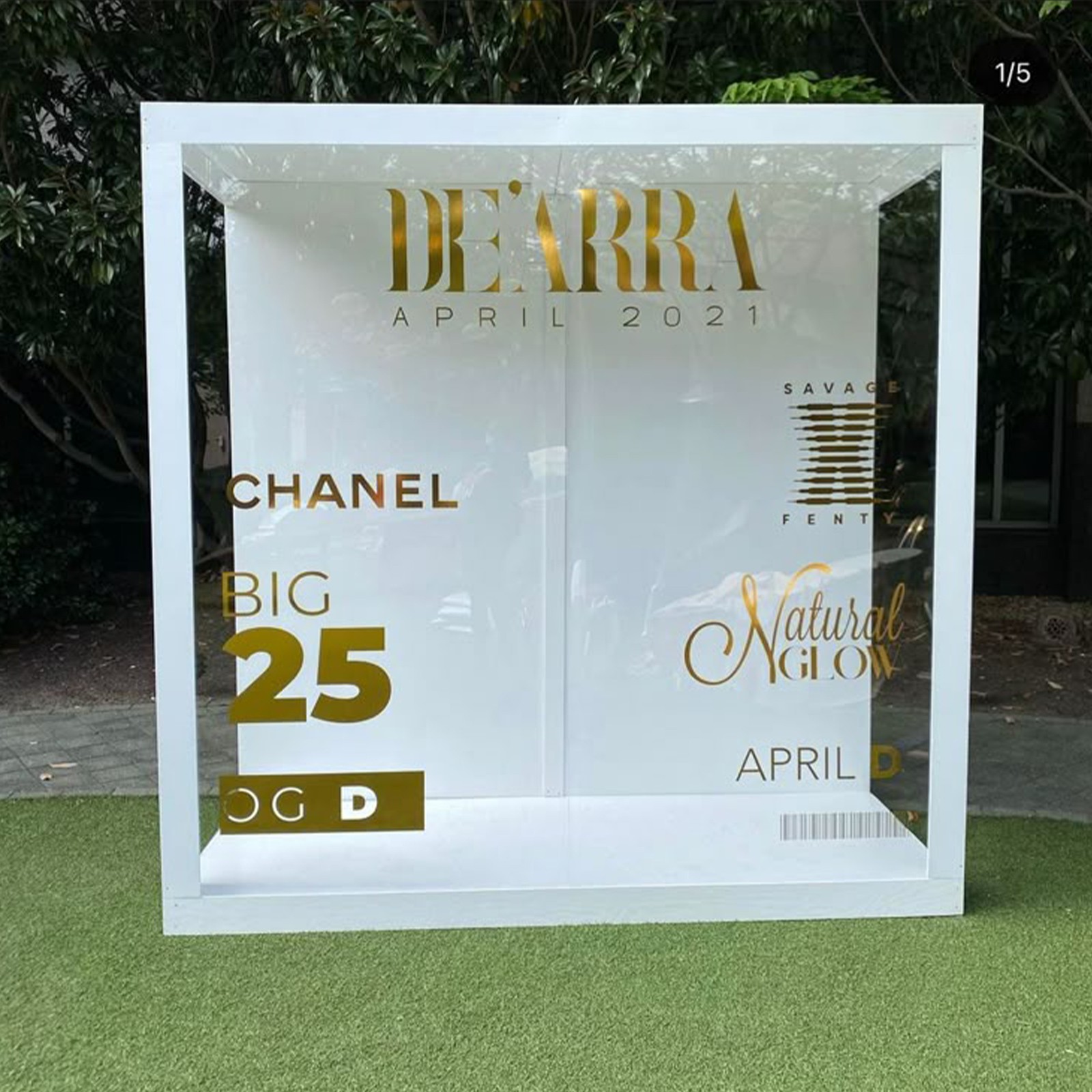

Interactive banner ads encourage user interaction through clickable elements, hover effects, or mini-games. This interaction engages users by allowing them to explore products or features actively, often making the ad experience more memorable.
Example: Mazda’s digital campaign for the Mazda2 featured a game called “Challenge the Night,” where users interacted with a car and learned about its features.
5. Transitional banner ads
Transitional ads change or adapt based on user interaction. The two most common types are:
Expandable Banners: These ads start small but expand when the user engages with them, revealing additional information.
Floating Banners: These move across the screen as the user scrolls down the page.
Example: A floating banner that appears subtly as users scroll, without interrupting their browsing.
Here are some key practices to ensure your banner ads are successful:
1. Use high-quality visuals
The visual design of your banner ad plays a crucial role in grabbing attention and presenting your brand professionally. Ensure that your images or graphics are high-resolution and visually appealing, while also aligning with your brand’s identity.
Example: The Adelphi Hotel uses vibrant, stunning images of its property in its banner ads, which help attract viewers and build trust in the brand's quality and attention to detail.

2. Place a logo
Including your brand logo in every banner ad is essential for brand recognition. A logo helps users quickly identify your brand as they browse, reinforcing your brand identity across multiple platforms. Consistent use of your logo across different ads and channels also strengthens your brand image and fosters trust.

3. Present a clear value proposition
In a highly competitive digital environment, a clear value proposition is crucial for grabbing attention. Ads that immediately communicate specific benefits or solutions are more likely to engage users. Focus on what you're selling, unique features, or any available promotions (like free shipping or discounts).
Consider the following questions when crafting your value proposition:
What product or service are you promoting?
Are there any standout features or promotions?
How does your product stand out from the competition?
Example: The service "Four" offers users the ability to split their purchases into four interest-free payments. Its banner ad presents a clear value proposition: "Shop now, pay later," followed by the subhead detailing "4 equal payments, interest-free."

4. Incorporate a strong call to action (CTA)
A compelling and clear call to action (CTA) is vital for encouraging users to take the desired next step, whether it's making a purchase, signing up, or learning more about a product. The CTA should be action-oriented, persuasive, and aligned with the ad’s value proposition.
Example: Shopify’s banner ads feature a concise value proposition: “Shopify has all the tools you need to start, sell, market, and manage.” The CTA, “Try Shopify Free,” is direct and motivates users to take immediate action by offering a risk-free trial.
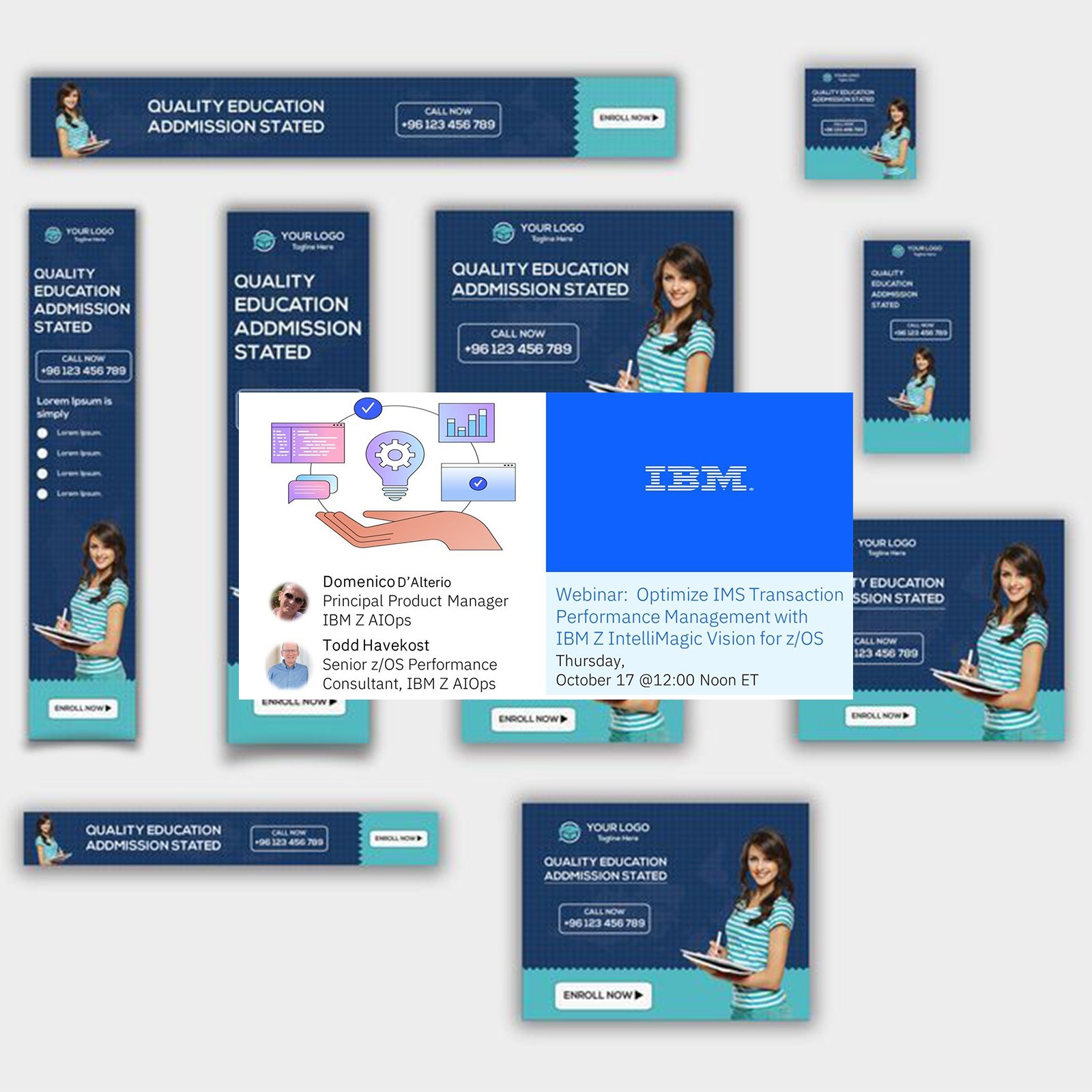
5. Maintain brand consistency
Ensuring consistency across all your banner ads helps build trust and familiarity with your audience. Using a consistent color palette, fonts, and imagery reinforces a unified visual identity, making your brand easily recognizable. Consistency across your ads also helps create a professional and cohesive look across different platforms.
Example: IBM maintains brand consistency by using the same logo, fonts, and design elements across all its web banners, strengthening its visual identity.

6. Choose a format and Size
Banner ad formats and dimensions vary based on the platform and the host website's specifications. Choosing the right format is key to maximizing visibility and engagement.
Here are the three most common formats for banner ads:
Leaderboard: A horizontal ad placed at the top or bottom of a webpage. Due to its wide size and prominent location, it’s ideal for grabbing attention.
Skyscraper: A vertical ad format typically found in sidebars or menus. Its tall, narrow shape is effective for long-form messaging.
Square: A balanced, compact format with equal dimensions, often used for more concise ads.
Regarding dimensions, Google responsive ads automatically adjust in size and format to fit various ad spaces. To use this feature, simply upload assets like headlines, descriptions, logos, and images, and Google will optimize and serve these ads across its Display Network.
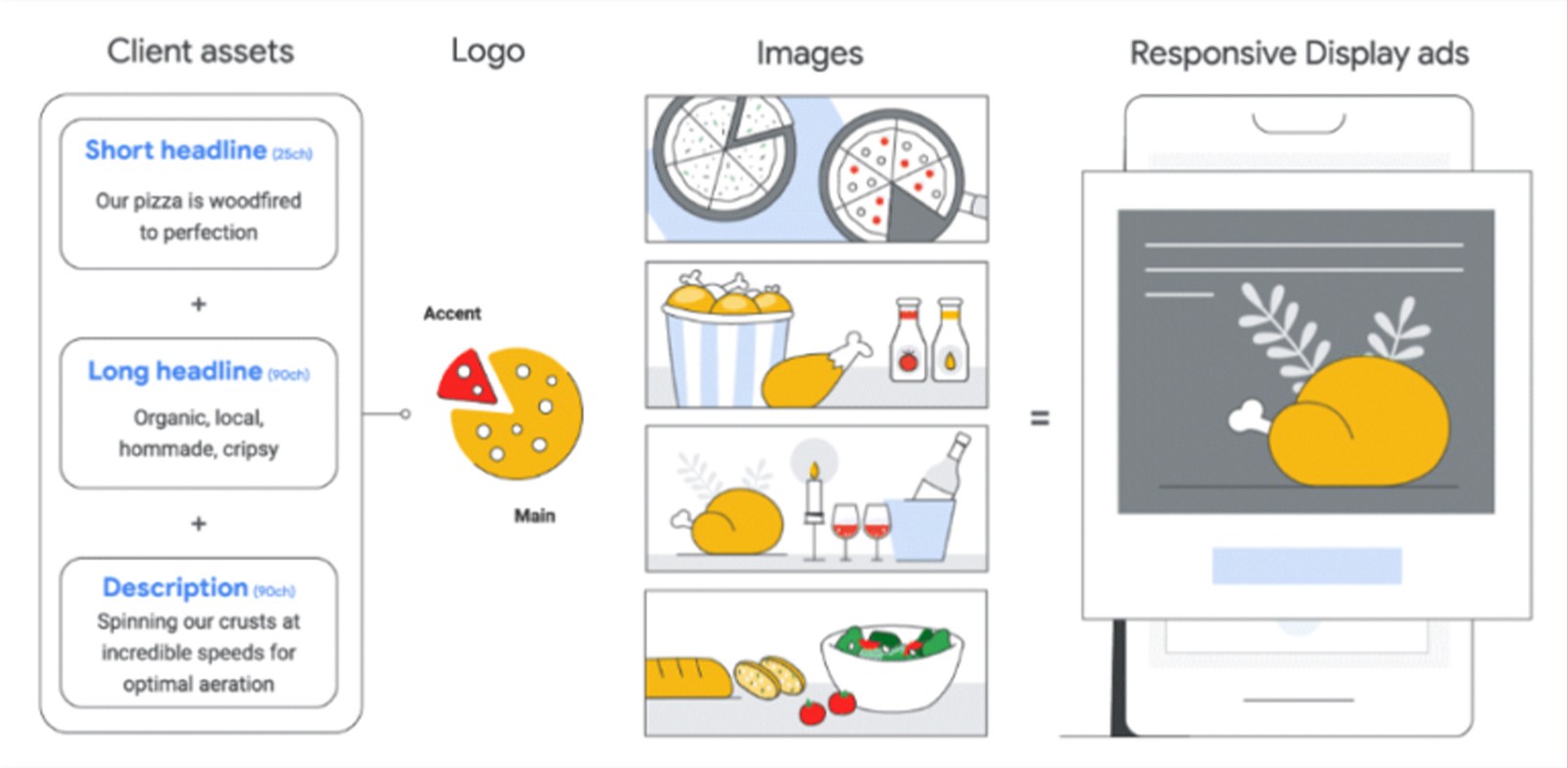
While ad dimensions can vary, it's best to design your ads with three standard sizes in mind:
Leaderboard (728×90 pixels)
Medium banner (300×250 pixels)
Wide skyscraper (160×600 pixels)
Google also provides general dimension guidelines for mobile devices and computers.
7. Use animations wisely
Animated banners tend to perform better than static ones, offering increased engagement, higher recall, and a 7% boost in conversion rates. However, it's crucial to use animations that complement, not distract from, your message. Opt for subtle effects like gentle fade-ins or product showcase loops to draw attention without overwhelming users.
Example: An animated food delivery service ad could show a rotating display of delicious dishes, enhancing the visual appeal and user experience.
8. Conduct A/B tests
Regularly testing different versions of your ads is key to improving their performance. A/B testing lets you compare variations in text, images, and backgrounds, giving you data-driven insights. Monitor metrics like click-through rates (CTR), conversions, and engagement to understand what works best, allowing you to make informed decisions for future campaigns.



























